There have been over 500+ international scientific studies. (See: National Library of Medicine - Type In Search Box: "Fucoidan".
The results are in: Fucoidan is fantastic!
Click Here: ORDERS
LARSON CENTURY RANCH, INC.
Fucoidan | U-Fucoidan/U-FN | Apoidan | U-Apoidan | | Limu Moui
P. O. Box 1982, Clarkston, WA 99403
Telephone: 509-758-5445, FAX: 509-758-5701
E-Mail: Sales@LarsonCenturyRanch.com
This page was last updated on: 3/23/2011
Copyright © 2004 Larson Century Ranch, Inc. ~ All Rights Reserved
Guest Book
All research done on Fucoidan indicates that it is completely safe to use and is nonallergenic; and it has no harmful effects on any bodily functions or organs.
DISCLAIMER: The Food and Drug Administration has not evaluated these statements. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
LCR Fucoidan - Modifilan - U-Fn (Capsules -- Powder)
Each capsule contains 500mg of concentrated Laminaria japonica (Brown Seaweed). Forty pounds of raw seaweed is needed to make one pound of LCR Fucoidan™.
This is a dietary supplement made from the richest variety of wild-grown brown seaweed (Hoku Kombu), and is gathered by hands of divers in its natural habitat. The seaweed undergoes a special patented low-temperature process, which takes away the heavy outer fibers from the luscious leaves and essentially "predigests" the Laminaria to make LCR Fucoidan™ especially bio-available.
This patented extraction technology makes bio-available the organic elements.
Click Here: ORDERS
Fucoidan -- Vital properties:
- Alginate: Natural absorbent of heavy metals. Detoxifies from lead, mercury, uranium and strontium. Alginate is classified as a hydrocolloid (a water-soluble biopolymer of colloidal nature when hydrated). Alginates are produced by brown seaweeds (Phaeophyceae, mainly Laminaria).
- Organic Iodine: Essential nutrient for a healthy life. Iodine obtained from kelp will not easily dissipate even after being heated for two hours, and it is more likely to be absorbed than inorganic iodine. Moreover, research on white rats proved that daily intake of 200 grams of organic iodine is safe.
- Laminarin: Laminaria Japonica Extract is made from the nutrient rich central vein of laminaria japonica; brown seaweed, and may help boost the immune system.
- Fucoidan: 40% Alginate. Fucoidan is a uniquely-structured sulfated polysaccharide (complex carbohydrate molecule) that is found in the cell walls of several types of brown seaweed, but not land plants. Its moisturizing property is what gives these seaweeds their slippery, sticky texture.
LCR Fucoidan ~ Modifilan
~ U-Fn: Processing
LCR U-Fucoidan (U-fn) is unique as the temperature during processing and production does not exceed 176 degrees F. This is significant because unlike other seaweed products available on the market which are processed as high as 212 degrees F. This means the Fucoidan retains it's natural micro-elements because they are not broken down by high temperatures, and makes LCR Fucoidan the most powerful and effective seaweed product available.
LCR LIMU PLUS (Liquid Nutrition)
Brought To You By: Vitacorp International
A Network Marketing Company
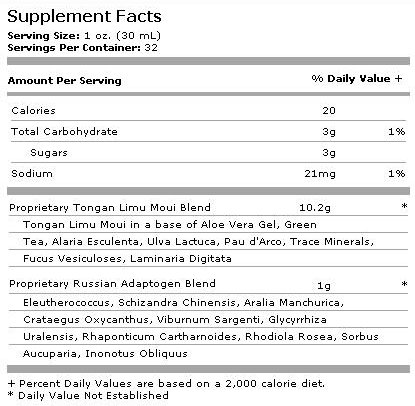
Limu Plus: 32 Servings
Click Here: ORDERS
Independent Distributor ID: 480017
Fucoidan... Powerful & Effective
LCR Fucoidan is unique as the temperature during processing and production does not exceed 176 degrees F. This is significant because unlike other seaweed products available on the market which are processed as high as 212 degrees F. This means the Fucoidan retains it's natural micro-elements because they are not broken down by high temperatures, and makes LCR Fucoidan the most powerful and effective seaweed product available.
Fucoidan Benefits
The brown seaweed in LCR Fucoidan is harvested from the clean, pristine waters of the northern Pacific ocean. Fucoidan has been tested worldwide, is bottled in the United States and is now available.
Laboratory studies show that fucoidan provides functional support to the immune system in a multitude of different ways. A robust immune system is the key to optimal health.*
Fucoidan... Dried Seaweed
Most commonly asked question:
Q. What is the difference between LCR Fucoidan and dried seaweed?
A. LCR Fucoidan is not dried seaweed. LCR Fucoidan is made from the nutrient-rich central vein of Laminaria Japonica; brown seaweed. The heavy outer fibers are sloughed off prior to processing. The rich nutrients remain. These nutrients are polysaccharides and are easily absorbed by our bodies because the seaweed is "predigested." (The stomach does not first have to break down the rough outer fibers.) Forty to fifty pounds of raw seaweed are needed to make just one pound of Fucoidan. Read more here: About Fucoidan
Read on for more LCR Fucoidan information.
Research Institute
Glycotechnology Advancement
Details concerning the Research Institute for Glycotechnology Advancement
With funding from the Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institute (a special legal person under the joint jurisdiction of the Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry and the Ministry of Finance), Aomori prefecture, Hirosaki city, as well as eleven private sector companies, the Research Institute for a Glycotechnology Advancement was founded in February 1991. The Institute ranks as a research organization operating under the auspices of the Intelligent Research Institute, a body that was formed as part of the overall efforts to promote the development of the Tohoku (northeast) area.
Name of research project: Glycobiology research aimed at the development of useful carbohydrates Research time span: 7 years (1990 to 1996)
Details concerning the Institute Research Institute for Glycotechnology Advancement
82-4 Oaza zaifu-cho
Hirosaki-shi
Aomori-ken
Japan
Research Institute
Glycotechnolgy Advancement
Research Fucoidan
Fucoidan is highly branched sulfated polysaccharides based mainly on L-fucose units. Fucoidan is distributed in the intercellular matrix in brown algae. They have anticoagulant and antithrombotic effects by inhibiting thrombin and modulate some cytokine secretion by binding receptor on immune cells. In addition, antitumor activity of fucoidan is related to the activation of macrophage-mediated tumor cell killing and interferes cancer cell metastasis by inhibition of physical interaction between the tumor cell and basement membrane. The objective was to establish the extraction condition of fucoidan from sea mustard and to investigate which molecular size of fucoidan has more effect on the activation of murine macrophage P388D1. Fucoidan was extracted from sea mustard, Undaria pinnatifida, with different pH, temperature, and time. The extracted fucoidan was fractionated with hollow fiber type ultramembrane filter (MWCO; 3, 10, and 30 kDa) to obtain fucoidan with different molecular size. P388D1 was incubated for 5 days with different molecular size of fucoidans with different concentration (0.1-1000 µg/mL). Cell proliferation was assayed by Trypan blue staining and cytoxicity was measured by MTT assay. Cytokines were assayed by Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western blotting. Our results showed that, optimum extraction conditions for the extraction of fucoidans from sea mustard were estimated to be at pH 1.0 and temperature 70oC for 3 hr. In the presence of 1-1000 µg/mL, fucoidan fraction having 3-10 kDa of molecular size significantly increased cell proliferation (p<0.05). However, fucoidan fraction having 30 kDa of molecular size showed inhibition of cell growth. These results suggest that extraction conditions for fucoidan from sea mustard will be applicable for the production of fucoidan from the brown algae. Macrophage proliferation will contribute on the commercialization of fucoidan products.
S. K. SEUL1, H. S. Shim2, S. B. Kim2, W. C. Choi1, M. J. Oh3, H. R. Kim2, and D. S. Byun2. (1) Department of Biology, Pusan National University, College of Natural Science, Busan, 609-735, South Korea, (2) Faculty of Food Science and Biotechnology, Pukyong National University, College of Fisheries Science, Busan, 608-737, South Korea, (3) Department of Fish Pathology, Yosu National University, Yosusi, Chunnam, Yosu, 550-749, South Korea
FUCOIDAN, MODIFILAN, U-FN
Apoidan/Apoidan-U/Kombu
LimuPlus (Limu Moui) Sales
Alternative Medicine ~ Alternative Health, Dietary Supplements, Health
Health Foods, Health Products, Dietary Supplements, Nutrition,
Vitamin Supplements








There have been over 500+ International Scientific Studies. See: National Library of Medicine ...
Type In Search Box - "Fucoidan"
8 WELCOME - LCR FUCOIDAN


One of nature’s health secrets has been discovered in the waters off the coast of the Pacific island of Tonga. Here in this lush tropical paradise, untouched by industry and unspoiled by pollution, natives have known the energizing benefits of the sea plant they call limu moui.*
But Limu Moui is no ordinary plant. In addition to being packed with the vitamins, minerals and other life-giving substances that have made kelp such a health food staple, limu moui is particularly rich in Fucoidan, which according to research may lend extraordinary support to the body’s immune functions.
Adaptogens are a rare class of plant first identified by Russian scientists in their quest for the key to improved human performance. According to these researchers, they help restore the body’s overall capacity for exertion and resistance to stress.* As more people in the West learn about this exciting science, the interest in advanced adaptogens increases.
Recognizing the adaptogenic potential of Limu Moui, Vitacorp asked the question, "What would happen if we reinforced this traditional Tongan source of Fucoidan with a complex of advanced adaptogens?* The answer was a breakthrough product like no other!

Web: Design Carte

LCR FUCOIDAN
LCR Fucoidan/Modifilan
Apoidan
90 Gel Capsules 500mg
LCR U-Fucoidan PLUS (U-Fn)
Apoidan-U
60 Gel Capsules
600mg (See: U-Fn)
Also See: Seaweed/kelp
POWDER OR CAPSULES
AVAILABLE... INQUIRE (509-758-5445)
Limu Plus - Click Here: ORDERS
Limu Plus - Click Here: ORDERS

